How can we improve health and safety conditions in the workplace by using intelligent lifting equipment?
First and foremost, ensuring safe and healthy working conditions is crucial to setting sustainable standards for the working environment. Industries continue to be faced with frequent cases of occupational illness and accidents, the consequences of which in terms of human suffering and economic fallout remain significant.
Promoting health and safety in the workplace is essential to improving overall working conditions. This is of paramount importance, not only to ensure the well-being of workers, but also to have a positive impact on productivity. Healthy employees are more motivated, enjoy greater job satisfaction and contribute to the production of higher-quality goods and services. As a result, they also improve the overall quality of life for individuals and society as a whole.
Risk prevention
It's essential to set long-term goals for improving health and safety in the workplace. By striving to reduce the risks present in the working environment, we help to reduce the unfortunate and costly incidents associated with injuries and accidents, which in turn improves working conditions and boosts productivity.
Several factors influence health and safety in the workplace, such as ergonomics, stress and chemical hazards, all of which need to be taken into account. In all environments, there are rules that workers must follow. This article focuses on ergonomics, examining how tasks and working methods can be adapted to reduce the risk of accidents and protect workers' health. Sustainable work planning and organization are the key to successful risk prevention.
Since occupational hazards arise in the workplace, it is the employer's responsibility to ensure that the working environment is healthy and safe. This includes preventing and protecting workers from occupational hazards. Risk prevention education and training on how to perform tasks safely are essential elements in creating a healthy and safe workplace.
Identify and understand health and safety risks in the workplace
In general, small workplaces tend to have a higher number of workplace accidents than large spaces. It appears that the rate of serious injury in small companies (defined as those employing fewer than 50 people) is twice as high as that in large companies (defined as those employing more than 200 people).
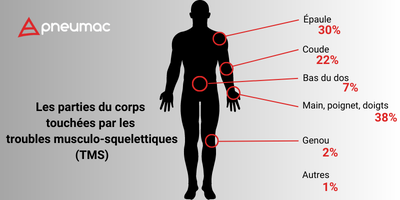
Whatever the size of the company, there is a close link between working conditions and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). MSDs occur in most industries, and are often associated with manual handling activities such as heavy lifting, repetitive tasks, awkward working postures and strenuous, stressful movements. Manual handling mainly involves manual lifting, carrying, pushing or pulling. It also includes tasks such as moving goods to and from shelves, sorting and palletizing packaging, manually filling mixers and machines with raw materials, etc. Heavy manual handling activities present risks to workers' backs, shoulders and arms, particularly when inappropriate working postures are involved.
Current ergonomic knowledge focuses on three aspects considered the most important for preventing back injuries:
- Avoid heavy lifting wherever possible (or use technical aids such as vacuum lifting systems or electric forklifts).
- Keep the load as close to the body as possible.
- Avoid twisting when lifting.
The human body is designed to move and carry loads, and even benefits from this diversity in terms of variations in loads and movements, which promotes recovery. When the same lifting movements or handling tasks are repeated frequently or over a long period of time, recovery possibilities are limited and the risk of illness or accidents increases.
What do we mean by "high-risk load"?
High-risk loads, or loads presenting a health hazard, include heavy loads, repetitive tasks, similar loads and static muscle work. The notion of "load dose" is often used to assess the risk of health problems or injury. Load dose is a combination of the following work-related factors:
- Intensity (how much)
- Frequency (how often)
- Duration (how long)
A high dose of load is often associated with high risk, but even low doses of load can have adverse effects on health, especially when the work is repetitive. Repetitive work refers to the performance of one or more tasks (with similar movements) repeatedly over a large part of the working day. Typically, the task is only one part of a larger workflow, and is often performed at a fast pace.
Constant repetition of the same movements creates a uniform, constant load. In this case, the weight of the object being handled is of little importance, as the sheer weight of the arms places an unfavorable strain on muscles and joints. In the long term, this can lead to the progressive onset of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), which can take a long time to heal. Once injured, it's common to feel the same pain when re-exposed to similar loads.
What are the employer's occupational health and safety responsibilities?
Employers are responsible for ensuring that the workplace and the tasks to be performed are ergonomically designed. To implement preventive measures, employers must examine working conditions and carry out a risk assessment.
When an employee is injured as a result of acute overload during a task, or suffers from an occupational illness due to prolonged overload, the employer must intervene. The sooner action is taken, the easier it will be for the employee to return to work.
Employers should assess whether loads, individually or in combination, present a risk of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). Risks should be assessed in relation to the duration, frequency and intensity of the load (as mentioned above). In addition, the employer must design the workplace to minimize the risk of MSD when manually handling loads.
Implementing preventive measures involves both organizational processes and the use of lifting aids such as vacuum lifting systems and electric forklifts, to avoid workers having to handle loads manually.
What are the employee's occupational health and safety responsibilities?
Employees also have responsibilities. Being alert to hazards in the working environment and reporting them to their employer is an obligation. To prevent the risk of accidents, injuries or MSDs, employees must also use protective aids and equipment in accordance with the employer's instructions on how to carry out the work.
Using TAWI lifting equipment as a preventive measure
As previously mentioned, it is advisable to avoid manual handling and heavy lifting in order to prevent injuries and accidents in the workplace. However, avoiding manual handling may not be possible by reorganizing a specific task, and in such cases employers should look for alternative solutions. Lifting aids, such as mobile and/or fixed vacuum lifting systems, electric stackers and hoists, are just a few examples of equipment that not only minimize the risk of injury, but can also help boost productivity.
By combining improved health and safety at work with increased productivity, your company can secure a sustainable future. This is precisely what TAWI strives to help you achieve. Their intelligent lifting equipment is designed to optimize your workflow, whether in production, distribution or logistics.